Research Area of Data Mining Lab
Our Vision
Our research group focuses on personalized machine learning, personalized search or information retrieval, and lightweight and scalable data mining, with particular emphasis on graph-based methods and language models. We aim to design effective and efficient algorithms for analyzing real-world data, with a central interest in modeling relationships among entities in complex and dynamic datasets. Our work supports practical applications in personalized recommendation, intelligent search, knowledge discovery, and AI agents.
Personalized Machine Learning and Recommender Systems
Q. How can we represent individual user preferences in a scalable and generalizable way? What kinds of user data are most useful for personalization? How can we adapt personalized models to dynamic user preferences and concept drift?
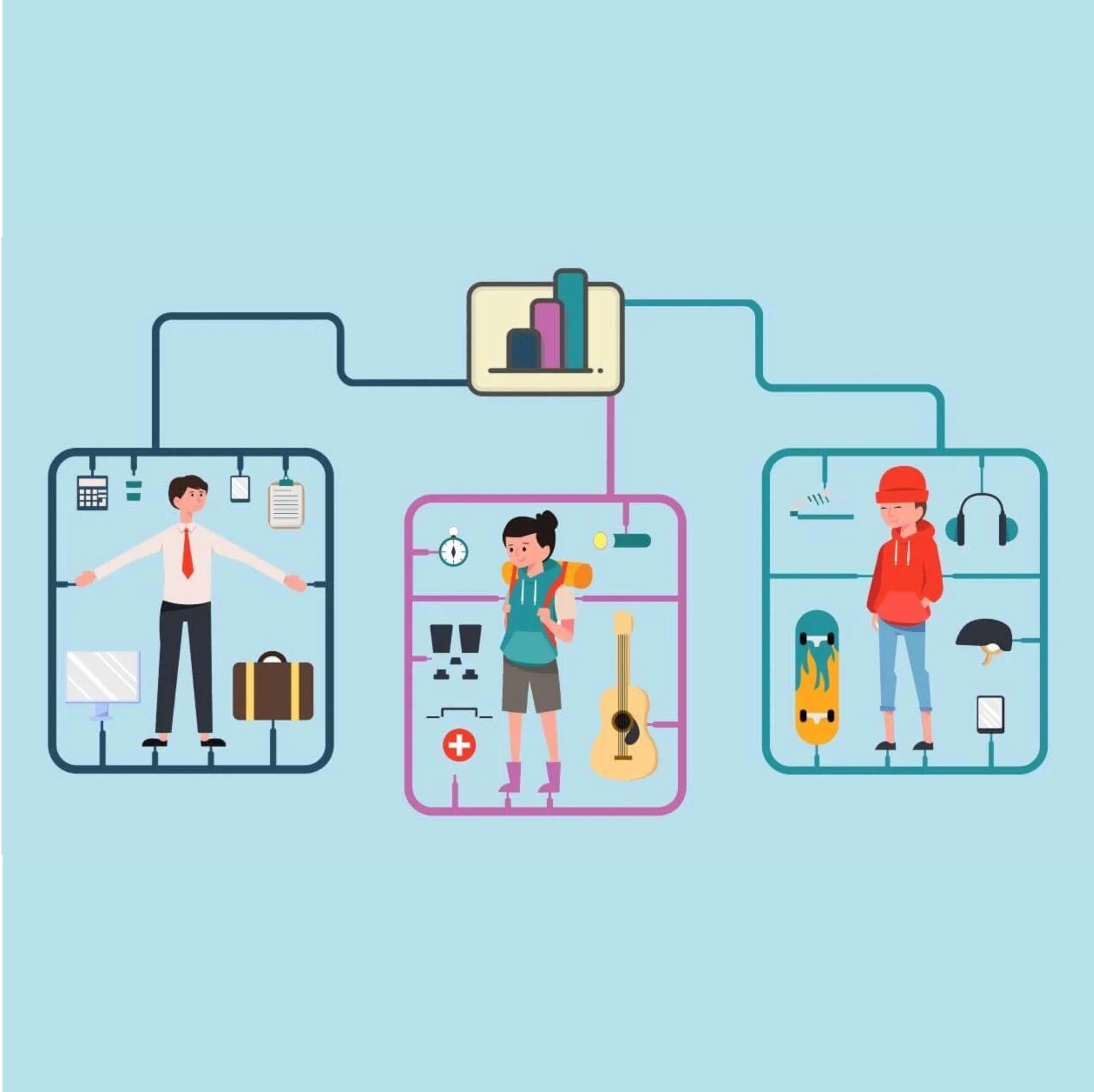
We develop ML methods that effectively represent individual user preferences in a scalable and generalizable way. Our research leverages user-centric signals, including behavioral patterns, contextual information, and temporal dynamics, to build adaptive models that personalize experiences across diverse tasks. We integrate graph-based architectures, sequential modeling, and multimodal representations to capture the complex and evolving nature of user–item relationships. To address concept drift and changing user interests, we explore continual learning strategies that enable models to adapt over time. These approaches form the foundation for robust personalized systems, supporting applications such as recommendation, search, and user-aligned AI agents.
Publications
- MuLe: Multi-Grained Graph Learning for Multi-Behavior Recommendation, CIKM 2024
- Accurate Node Feature Estimation with Structured Variational Graph Autoencoder, KDD 2022
- A comparative study of matrix factorization and random walk with restart in recommender systems, BigData 2017
- Personalized Ranking in Signed Networks using Signed Random Walk with Restart, ICDM 2016
Graph Machine Learning
Q. How can we better understand the relationships between people, items, or ideas by modeling them as networks or graphs? How can we design graph learning models that effectively capture the complex and dynamic structure of real-world relational data?
Graphs represent attributes of entities and their relationships in complex systems such as social networks, hyperlink networks, knowledge graphs, user-item networks, molecular graphs, and biomedical networks as well as modeling 3D objects in a point cloud, connections of computer systems, and function calls in source code. Graph ML is an emerging research area, which aims at learning deep representation on graphs for a wide range of applications from recommender systems and natural language processing to drug discovery and fraud detection. In this project, we work on designing machine learning methods for real-world graphs modeling complex, dynamic, and richly-labeled relational structures.
Publications
- PIGLET: Probabilistic Message Passing for Semi-supervised Link Sign Prediction, ICDM 2025
- AugWard: Augmentation-Aware Representation Learning for Accurate Graph Classification, PAKDD 2025
- Time-Aware Random Walk Diffusion to Improve Dynamic Graph Learning, AAAI 2023
- Learning to Walk across Time for Interpretable Temporal Knowledge Graph Completion, KDD 2021
Lightweight and Scalable Data Mining
Q. How can we design data mining algorithms that are both lightweight and scalable for analyzing large and complex datasets?
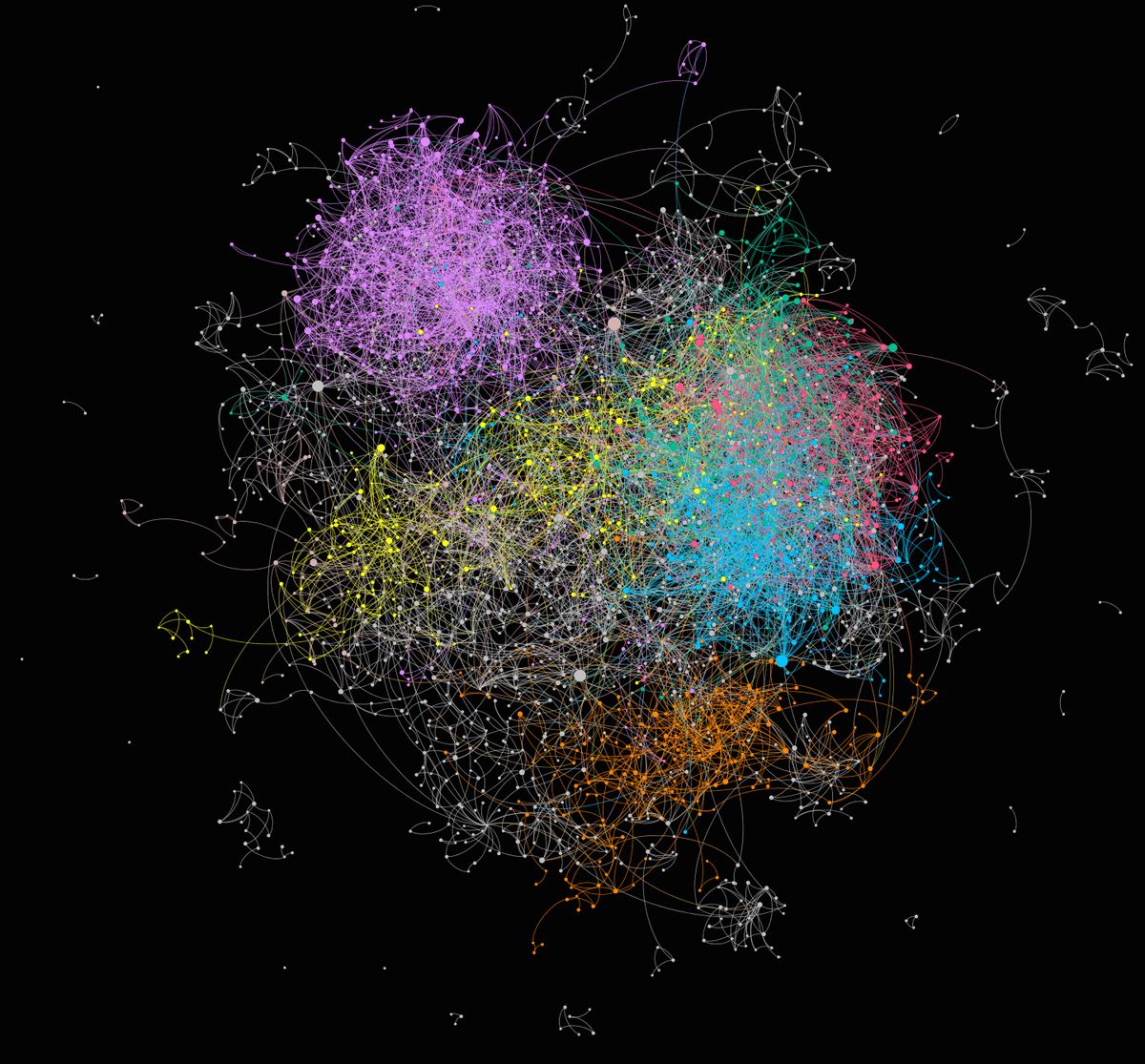

This research develops lightweight and scalable data mining methods for extracting patterns and knowledge from large, complex datasets under limited computational resources. We focus on compact models, approximate computing, and graph-based representations to ensure efficiency across diverse tasks. Target applications include on-device AI, scalable recommendation, graph search, stream-based event detection, and anomaly detection. By balancing accuracy and efficiency, our work enables adaptive, real-time intelligence in resource-constrained and large-scale environments. Ultimately, we aim to make intelligent systems more accessible, deployable, and responsive across real-world settings.
Publications
- Effective and Lightweight Representation Learning for Signed Bipartite Graphs, NN 2025
- ELiCiT: Effective and Lightweight Lossy Compression of Tensors, ICDM 2024
- Compact Decomposition of Irregular Tensors for Data Compression: From Sparse to Dense to High-Order Tensors, KDD 2024
- TensorCodec: Compact Lossy Compression of Tensors without Strong Data Assumptions, ICDM 2023